[N]o other class of medications in virtually all of medicine inspires more baseless fears, intentional disinformation, and wild beliefs as do the stimulants used to treat ADHD.
Interestingly, these fears are almost entirely an American phenomenon that hardly exists elsewhere in the world.
[H]aving ADHD lowers a person’s estimated life expectancy by 12.7 years.
From other articles on the site:
-
ADHD medication use lowers risk of death by 19%, risk of overdose by 50%, and it reduces hospitalizations
-
[T]he risk of substance abuse decreases substantially when [ADHD] patients are treated with stimulant medication

deleted by creator
Pervitin!
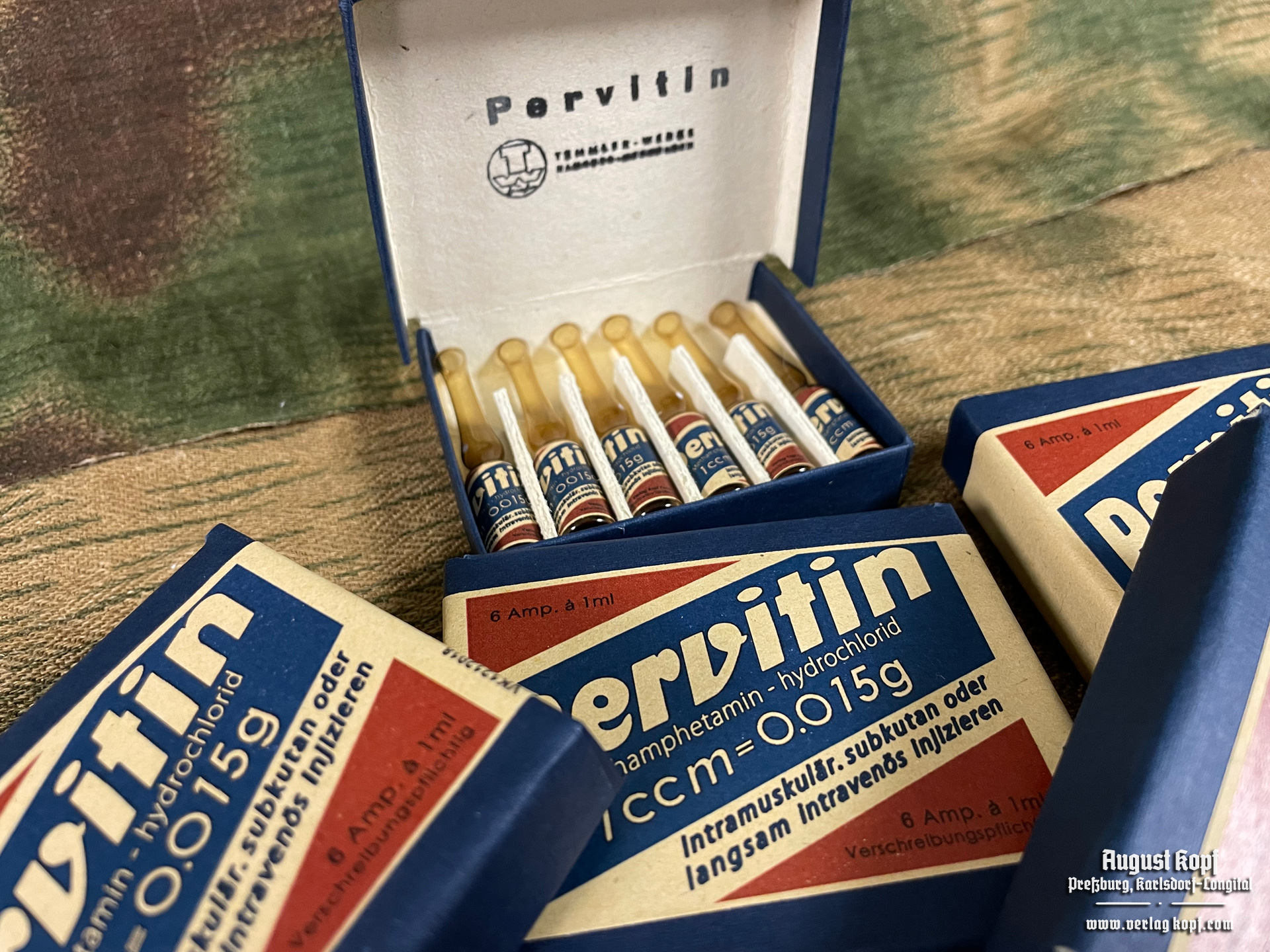
There’s an interesting and easy read on amphetamines used in Nazi Germany titled Blitzed by Norman Ohler. You know where to find the ebook but TankieTube has the full audiobook here
Fun fact: doctors in the US still occasionally prescribe methamphetamine for ADHD. It goes by the trademark name Desoxyn.
deleted by creator
I think methamphetamine is less neurotoxic than amphetamine at the equivalent dosage, although that’s only what I heard - never looked into it to say that I know this for a fact.
Did you know that Ohler has a new book out called Tripped about psychedelics? It’s also up on TankieTube as an audiobook here although I haven’t read it yet but based on Blitzed I’d assume it’s pretty good.
deleted by creator
If you do give it a listen I’d love to hear your thoughts on it
deleted by creator
Awww yis! We got a book review/infodump in the pipeline!!
deleted by creator
Excellent summary so far. Is it meeting your expectations?
deleted by creator
Iirc blitzed says meth was very common among the German populace before the war.
deleted by creator
Amphetamines are easier to synthesize than coffee is to brew? Really?
I suppose you mean once you have the precursors?
deleted by creator
deleted by creator
deleted by creator
Amphetamines are easier to synthesize than coffee is to grow I think is what they mean
deleted by creator
If you’re talking about my bio, it’s just a reference to Bo Burnham’s Inside. But because it came out in 2021 I changed the number lol
deleted by creator